ASIC and FPGA design advantages and process comparison
ASICs and FPGAs each bring unique strengths to the table, and it's essential to understand their differences before making a decision. There is a wealth of information available when comparing these two technologies, and here’s a detailed look at their respective advantages and disadvantages.
Design Advantages: FPGA vs. ASIC
FPGA Design Advantages | ASIC Design Advantages
Faster time to market – no need for complex manufacturing steps like wiring or masking. | Full custom performance – designed specifically to meet exact specifications.
No NRE (Non-Recurring Engineering) costs – no upfront design expenses. | Lower unit cost for high-volume production.
Shorter design cycles – software handles most layout, routing, and implementation tasks. | Smaller form factor – optimized for space efficiency.
More predictable project timelines – fewer risks of re-spins or wafer delays. | Higher internal clock speeds – ideal for performance-critical applications.
Field reprogrammability – can be updated remotely with new configurations. |
In the past, FPGAs were typically used for low-speed, low-complexity, or small-capacity designs. However, modern FPGAs have evolved significantly and can now easily exceed 500 MHz in performance. With increased logic density, advanced features like embedded processors, DSP blocks, and high-speed serial interfaces, FPGAs are now a go-to solution for a wide range of applications, often at a more competitive price than traditional ASICs.
Design Flow Comparison: FPGA vs. ASIC
The FPGA design flow streamlines the process by eliminating many of the time-consuming and complex steps involved in ASIC design, such as layout, routing, timing analysis, and mask re-spins. This is because the core logic is already pre-integrated into the FPGA device, which has been thoroughly tested and validated.
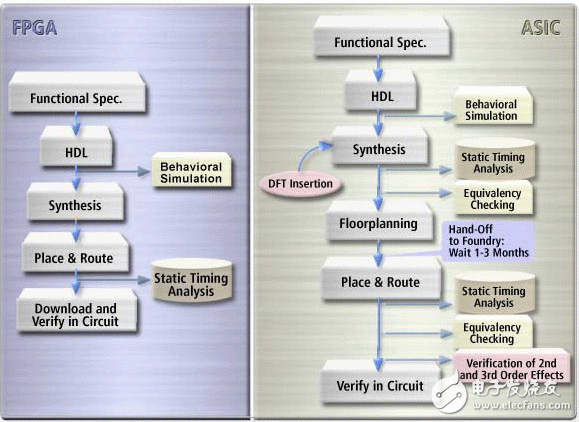
That said, Xilinx and other FPGA vendors provide powerful tools like advanced floorplanning, hierarchical design capabilities, and sophisticated timing analysis to help users push the limits of FPGA performance. These features make FPGAs suitable not only for prototyping but also for high-performance applications that once required ASICs.
SVLEC offers a variety of cables designed to support industrial protocols including AS-I, Can Open, Device Net, Ethernet/IP, Ether CAT, Profibus, Profinet . Based on customers' request , the cable length can be any meter .



Field Bus,M12 A-Code Connector,M12 Profibus Cable,Custom Devicenet Connection Cable
Kunshan SVL Electric Co.,Ltd , https://www.svlelectric.com