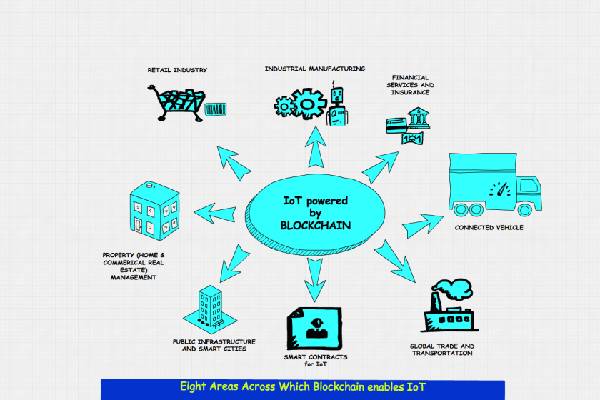
The blockchain and the Internet of Things are a natural fit and can provide many application scenarios and use cases for the Internet of Things. These possibilities are no longer futuristic, we can discuss them at the moment. Internet of Things encounters blockchain There is no doubt that the blockchain and the Internet of Things are two hot words in the current technology field. The Internet of Things contains moving objects such as sensors and vehicles. It basically covers any device that uses embedded electronic components to communicate with the outside world, especially the IP protocol. Combining it with the blockchain is beneficial to the entire life cycle of IoT devices and applications, and is an auxiliaries for business processes. Imagine a scenario where a networked driverless car can use the private chain to ensure real-time secure communication of the vehicle, including car start, driver identification, smart contract exchange insurance and repair service information, real-time location information, and tracking of vehicles. Distributed ledger technology based on blockchain fills five key defects of the Internet of Things 1. In the above typical scenario, a distributed ledger based on a blockchain can provide trust, ownership records, transparency, and communication support for the Internet of Things; 2. It should be noted that the IoT community will develop a private chain in a few years to save transaction information in an extremely secure manner. The IoT architecture that collects and stores data using a centralized server can write information to local books and synchronize with other localized books to ensure the security and uniqueness of the facts; 3. Add timestamps to all IoT transactions on the blockchain to ensure that future generations are available; 4. The real innovation of the blockchain lies in digital protocols or smart contracts, which can be applied to blockchain data and enforce commercial terms in IoT communications; 5. One of the biggest drawbacks of the Internet of Things is that security standards are not in place. A blockchain with high-end encryption technology can solve security problems. IoT vertical application case in this context 1. Industrial manufacturing: The manufacturing cycle begins to enter a completely virtual world, including product development, customer demand monitoring, production, and inventory management. As devices and systems become more intelligent and interactive, the blockchain will become a book at the factory, regional, and global supply chain levels. Thereby greatly reducing costs, strengthening just-in-time production (JIT), better use of plant capacity, and improving operational efficiency; 2. Connected driverless cars: Connected Vehicles turn vehicles into huge smart applications. Car automation has been strengthened year by year, including navigation and road rescue. The blockchain will use digital networks to track these devices, enabling automatic tracking of vehicle-to-vehicle communications and insurance terms, annual vehicle inspections, etc. 3. Transportation: Internet of Things + blockchain = networked traffic. There are many application scenarios in the vehicle network, which can transmit all traffic information and avoid traffic jams and other issues. Extending it to global trade, this transportation network can include water, air and ground transportation networks to track cargo transportation; 4. Public technical facilities and smart cities: Intelligent devices have been used to track the status of bridges, roads, power grids, etc. Blockchains can connect all of these together, share high efficiency, maintain, predict usage and pollution. Another important application is to help remote areas monitor natural disasters and prevent large-scale mountain fires, pests and other major disasters; 5. Financial services and insurance: Banks can use the blockchain to track IoT devices, such as ATMs, and maintain them. Insurers that have used drones to make property insurance claims in remote areas can use blockchain verification and verification claims; 6. Family and commercial real estate management: use smart sensors in housing and commercial buildings to achieve smart home and office monitoring; the use cases in the two areas are different, but the scope of application is large, and the basic functions of distributed ledgers can be integrated; 7. Smart Contracts: Blockchain-based cryptocurrencies can implement two advanced business functions: one is cryptocurrency transfer and the other is a business rule that stipulates the time of payout, especially in accordance with the terms. These rules, known as "smart contracts," apply to all of these business areas, can track business rules, and act on preset thresholds. For example, a driverless car that has not passed the annual inspection must be turned off. If the owner does not pay the premium, he will send a notice to the owner's housing association; 8. Retail: Retailers have used IoT devices and terminals in the business cycle. Including store floor, tracking store delivery, understanding customer transportation, wearables, etc. Networked storefronts add shelves to the Internet of Things to reduce inventory time. Blockchain enhances all use cases, enabling important connections between retailers and consumers, and automating the removal of intermediaries, whether they are issuers or central servers. For example, consumers can store product information and dimensions in a blockchain, and retailers can obtain relevant data securely and directly. Finally, it must be said that the blockchain technology is still flawed. Whether it is the underlying public chain of Bitcoin or Ethereum technology, there are defects in interoperability, security standards, throughput and developer tools. The next step is to solve these problems before implementing the production-level deployment of the Internet of Things on the blockchain. 600W Medical Power Supply,600W Medical Device Power Supply,600W Medical Power Adapter,600W Rade Power Supplies Shenzhen Longxc Power Supply Co., Ltd , https://www.longxcpower.com