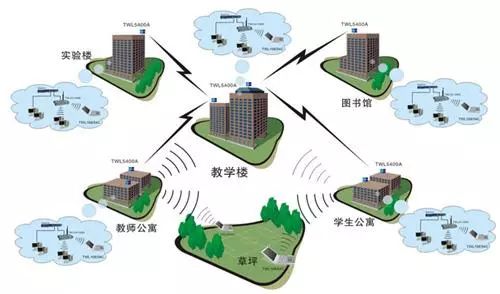
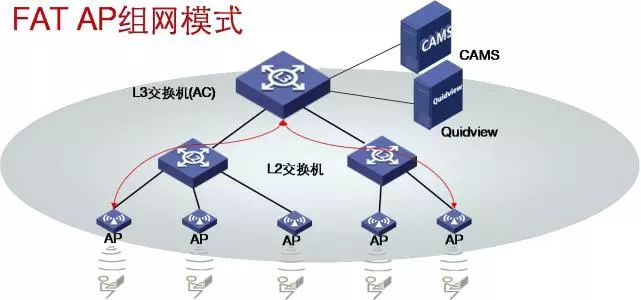
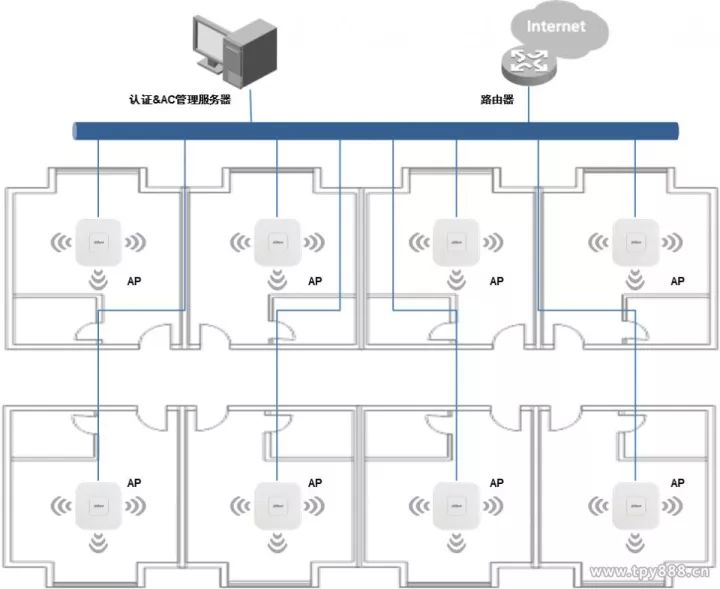
Citation A wireless AP is an access point that uses wireless devices (mobile devices such as mobile devices and laptops and other wireless devices) to access wired networks. It is mainly used in broadband homes, buildings, campus interiors, campus interiors, warehouses, and factories that require wireless monitoring. Local, typical distance covers tens of meters to hundreds of meters, but also can be used for long-distance transmission, the farthest can reach about 30KM, the main technology is IEEE802.11 series. Most wireless APs also have an AP client, which allows them to connect wirelessly with other APs and extend the network coverage. When setting up a wireless network, it is sure to encounter such a problem: How can we accurately predict the demand for wireless APs after examining the environment? With this question, we will discuss how to use bandwidth estimation. Wireless AP deployment. Factors affecting the number of wireless APs When estimating the number of wireless APs, four points need to be clarified, namely, network bandwidth, throughput, AP coverage distance, and number of access users. The impact of these points on the number of wireless APs is described below. 1, network bandwidth When the bandwidth of a link is usually discussed, it refers to the number of bits per second that can be transmitted on the link, and the maximum rate that can be achieved is emphasized. For example, the bandwidth of 100M Ethernet is 100Mbps, and the bandwidth of Gigabit Ethernet is 1000Mbps. 2, throughput Throughput and bandwidth are easy words to confuse. When discussing the bandwidth of a communication link, it generally refers to the number of bits per second that can be transmitted on a link. It depends on the link clock rate and the channel coding, which is also called line speed in a computer network. The bandwidth of Ethernet is 100Mbps. The difference between bandwidth and throughput: The bandwidth emphasizes the maximum speed that can be achieved, while the throughput emphasizes the speed in the actual situation. Since reality is affected by various inefficiencies, it is usually more preferred to use “throughput†to express the performance of the network. 3, coverage In a non-high density area scenario, consider the number of wireless APs based on the actual scene area and the recommended coverage area, and roughly determine the number of APs. In some cases, the maximum coverage distance can also be calculated, and the coverage can be appropriately adjusted according to the power. 4, the number of access In the high-density area scenario, the number of access users needs to be taken into account. Different types of wireless APs have different numbers of recommended users in different scenarios. The number of concurrent access users can be used to determine the number of wireless APs (notebooks and mobile phones are slightly different). Bandwidth calculation number of wireless APs Many friends are often asked by customers about this problem: In this scenario, this solution deploys so many APs. The bandwidth support is not supported. If it is not supported, then the user's network speed is not changed to the speed of the turtle, or the AP is deployed. How much export bandwidth is needed? 1. Export bandwidth can be obtained based on the number of APs, the maximum number of concurrent users, and the bandwidth allocated by each user. WLAN capacity bandwidth = maximum number of concurrent users × per user bandwidth. 2. The maximum number of concurrent users can be estimated from 50% to 70% based on the number of people who cover the scenario. 3. In order to allow each wireless terminal sufficient bandwidth to be available, a wireless AP is generally recommended to access 10 to 15 wireless networks (taking the RD-W25AP as an example, according to the recommended number of accesses in the above table). 4. The number of APs = the maximum number of concurrent users ÷15 (the number of users that a single AP accommodates). 5, each user's allocated bandwidth can generally set an intermediate value, calculate and estimate, such as 100kbps. (Common unit conversion: 1TB = 1024GB, 1G = 1024MB, 1MB = 1024KB, 1KB = 1024B, 1 byte = 8 bits.) For example: The number of users in a university is 30,000, and the number of mobile terminal users is 15,000. The concurrent rate is calculated as 50%-70%. The bandwidth per user is 512Kbps. The approximate WLAN capacity and number of APs are required. answer: 1. Concurrent access number = 15000x (50% ~ 70%) = 7500 ~ 10500 people; 2. Number of APs = maximum number of concurrent users ÷ 15 = (7500 10 10500) ÷ 15 = 500 700 700; 3, WLAN capacity requirements = (7500 ~ 10500) × 0.512 = (3840 ~ 5376) M. Virtual network application bandwidth calculation When many people do project demonstrations, they will intuitively connect WiFi test speeds through the device, but the speed of downloading can also easily estimate the theoretical broadband speed of the corresponding application. Network speed unit: Bps: Bits per second, usually bps for serial bus devices, such as serial ports, USB ports, Ethernet buses, etc. Bps: Bytes per second, usually Bps for parallel bus devices, such as parallel port, IDE hard disk, etc. Conversion relationship: 100M bps ≈ 10M Bps In general, if we say that the network speed is 100 megabits, that means 100 megabytes bps. If you download software from the Internet, the displayed speed unit is Bps, which is the number of bytes downloaded per second. Therefore, it must be clear that the unit of the speed of the network in different situations is not the same and cannot be mistaken because the speed difference between the two representations is more than 10 times. In the computer network and IDC room, the unit of broadband speed is expressed by bps (or b/s); the conversion relationship is: 1Byte=8bit 1B=8b ---------- 1B/s=8b/s (or 1Bps=8bps) 1KB=1024B ---------- 1KB/s=1024B/s 1MB=1024KB ---------- 1MB/s=1024KB/s Broadband download maximum theoretical value: 1.5 M =169 KB/s 3 M =338 KB/s 6 M =676 KB/s 10 M =1126 KB/s In practice, when downloading software, it is often seen when downloading software that the download speed is displayed as 128 KB (KB/s), 103 KB/s, etc., because the unit of the bandwidth provided by the ISP is bits, and the software is generally downloaded. The byte (1 byte = 8 bits) is displayed, so the actual value can be obtained by scaling. However, we can use the conversion formula to convert it: 128KB/s=128×8(Kb/s)=1024Kb/s=1Mb/s: 128KB/s=1Mb/s Theoretically: The theoretical rate of 2M (ie, 2Mb/s) wideband is: 256KB/s (ie, 2048Kb/s), and the actual rate is about 80-200kB/s; (The reason is due to user's computer performance, network equipment quality, resource usage, The impact of many factors such as the peak period of the network, website service capabilities, line attenuation, signal attenuation, etc.). The 4M (ie 4Mb/s) broadband theoretical rate is: 512KB/s, the actual rate is about 200---440kB/s The uplink rate refers to the data transmission rate when the user computer sends information to the network, and the downlink rate refers to the transmission rate when the network sends information to the user computer. For example, using FTP to upload files to the Internet will affect the upload speed is the "upstream rate"; and download files from the Internet, affect the download speed is the "downstream rate." Of course, in the actual uploading and downloading process, the quality of lines, devices (including computers and other devices) will also have a more or less impact on the speed. The above data is mainly caused by the influence of many factors such as user's computer performance, network equipment quality, resource usage, network peak period, website service capability, line attenuation, and signal attenuation. New Arrival or New Style Disposable ecig have a completely enclosed design, reducing the need for charging and replacing cartridges. The no-charge design also reduces the occurrence of faults. It is understood that with rechargeable e-cigarettes, each cartridge needs to be charged at least once and the battery efficiency is extremely low, while the design of disposable ecig can solve this problem very well. New Arrival Disposable E-Cigarette,New Arrival Mini E Cigarette,New Arrival Electronic Cigarette Customizing,Rechargeable E Cigarette Shenzhen E-wisdom Network Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.healthy-cigarettes.com