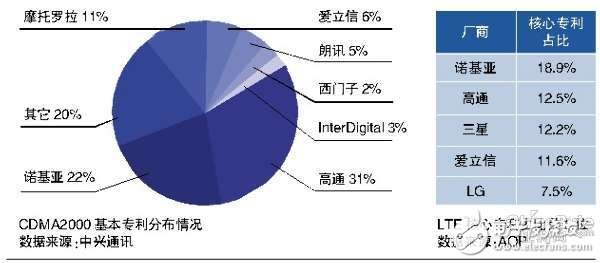
China's 4G era has really arrived. In the keynote speech of the 2013 Mobile World Congress, China Mobile made it clear that its TD-LTE network will cover more than 100 cities and 1 billion people across the country this year. LG, HTC, Huawei and ZTE have all actively released TD-LTE smartphones to support China Mobile's ambitious expansion. Moving towards 4G, Chinese smartphone manufacturers are trying to seize this opportunity to get rid of the 3G dilemma. On the surface, the Chinese smartphone market is a giant cake: research firm Canalys predicts that in 2013, China ’s smartphone shipments will reach 240 million units, double the United States and 1/3 of total global shipments. More than 60% of smartphone sales in China come from local brands. In fact, the digital glory cannot hide the cruel fact that the profit is meager or even loss-making. Nearly 800 local smartphone brands in China are struggling on the brink of profit and loss. Why is this so? In the 3G era, Chinese smartphone manufacturers face problems such as patent curbing, price wars hurting themselves, and low brand recognition: patent fees and patent barriers have overwhelmed Chinese smartphone manufacturers, and the direct consequence of compressing costs is that user experience is greatly reduced , So that the brand building effect is not good. Super Profiter Who is the beneficiary of the rise of the smartphone market represented by China? Needless to say, Apple and Samsung, Qualcomm, which originally stood in the background and did not directly face consumers, gradually entered the public's field of vision because of its absolute dominance in 3G patents. At present, most smart phones use the 3G communication standard, and 3G functions are standard for smart phones. After the CDMA market matured, Qualcomm cut off mobile phones, base stations and other services, leaving only the two strongest parts of the processor and IP authorization, concentrated on making money, and insisted on not reducing CDMA patent fees. Qualcomm holds a large number of CDMA standard basic patents (SEP), which is equivalent to opening up a new path, and this path is a must for many people to connect the two markets of smart phones and 3G. Road. Qualcomm is the toll collector at the entrance. The high patent licensing fees imposed on Chinese smartphone manufacturers are inescapable, whether it is for powerful smartphone manufacturers that cooperate directly with Qualcomm or MediaTek (MTK), or for mobile phone design house 3G PCBA (board card ) For small and medium-sized smartphone manufacturers, the only difference is how to pay and how much to pay. The reporter contacted several machine manufacturers such as HTC, Huawei, ZTE, Hisense, OPPO, etc. to try to understand the situation of patent fees, but these manufacturers are all secretive. Qualcomm has avoided the details of this one, but only said in general terms "Qualcomm's patent licensing model ensures that we continue to invest heavily in research and development." For the complete machine manufacturers who have the strength to directly contact Qualcomm and MediaTek, they pay a lot of patent fees. A senior insider in the mobile phone industry, who did not wish to be named, told reporters that when the whole machine manufacturer buys products provided by Qualcomm IP authorized chip manufacturers such as MediaTek, the patent fees carried are mainly divided into entry fees, platform fees and sales It consists of three parts, including: the entry fee is about 500,000 US dollars; the platform fee corresponds to each specific platform, and each platform needs to pay; the sales share is charged at 6% ~ 6.5% of the final product price of the machine manufacturer ( If the product is exported, this ratio will be higher than domestic sales). If the whole machine manufacturer chooses to cooperate with Qualcomm to buy its chips, there is no clear patent fee statement, but in fact these are included in the price of chips that are much more expensive than MediaTek. Most of China's first-line mobile phone manufacturers have not only picked up the goods from Qualcomm, but also maintained cooperation with MediaTek to ensure the richness of the product line. As small and medium-sized smartphone manufacturers, they are more inclined to purchase terminal PCBA products of mobile phone design houses for terminal integration. Wu Lingyun, founder and CEO of Shenzhen Mobile Club, told reporters that taking the 3G processor MTK6577 currently used by most domestic small and medium-sized smartphone manufacturers as an example, the cost of smartphones using this platform can be controlled at around 500 yuan (in the three major modules, the motherboard Depending on the configuration, the cost is between 300 yuan and 350 yuan, the cost of the display is about 100 yuan, and the cost of the camera does not exceed 70 yuan). The wholesale price of such a smartphone is about 580 yuan to 600 yuan, and the 3G patent licensing fee allocated to the mobile phone is 3 to 5 US dollars (about 20 to 33 yuan), that is, the patent licensing fee accounts for 20% of the gross profit. ~ 40%. I have to mention the agreement reached between MediaTek and Qualcomm: MediaTek does not pay Qualcomm IP licensing fees, but reports chip shipment numbers to Qualcomm. Qualcomm checks the shipment figures of agents and customers (including machine manufacturers and mobile phone design houses) based on the shipment figures reported by MediaTek, and then collects royalties based on the verified figures. Qualcomm knows the number and whereabouts of all chips sold. Another possibility is that manufacturers use a combination of "application processors and modem modules". According to the aforementioned insider, some domestic mobile phone manufacturers use application processors from Samsung, and the modem module is from Intel. It seems that it does not need to bow to Qualcomm, but in fact the modem module contains the results of cross-authorization between Intel and Qualcomm. Qualcomm Still profited from its patents. According to the aforementioned insiders, the current shipments of major smartphone chip providers are: MediaTek 17 million pieces / month (including WCDMA and Edge versions), Qualcomm 12 million pieces / month, Spreadtrum without paying royalties to Qualcomm And Intel are 7 million pieces / month (non-WCDMA standard, Edge version and TD version), 800,000 pieces / month. This comparison explains why Qualcomm ’s patent licensing fee income was as high as US $ 6 billion in 2012. Struggling in the big market In terms of production and sales, China is the most high-profile region in the smartphone industry. There is reasonably exciting opportunity for such a big market, but for Chinese smartphone manufacturers, the reality is not satisfactory. According to Canalys statistics, smartphone brands ranked by sales in China are Samsung, Lenovo, Coolpad, Huawei, and ZTE. The result of the iiMedia survey is that in the first quarter of 2012, 43.3% of the smartphones sold in the Chinese market were priced at less than 1,500 yuan, and high-end devices with more than 3,000 yuan accounted for 15.5% of total sales. An important reason why Chinese local smartphone manufacturers occupy 60% of the strong domestic market share is low prices. The strategy of Chinese manufacturers has always been to quickly gain market share at low prices, but in the dominant low-end market, consumers are extremely sensitive to prices, and manufacturers must rack their brains to control costs before they can hold onto existing sites. House seemingly endless rain. Almost all Chinese smartphone manufacturers that need to strictly reduce costs use Android. "Android requires higher hardware than iOS, which is also a factor that weakens the long-term profitability of Chinese mobile manufacturers." Therefore, a report released by the market research organization Sano said that domestic brands earn 1% of the profits of the Chinese smartphone market, and Samsung and Apple took 99%, which is not surprising. Chinese smartphone manufacturers firmly believe that the market share will rise, and the R & D expenses, sales expenses, and production costs of individual products will be reduced because of the right to speak in the industrial chain. Larger smartphone manufacturers want to further profit through application stores and value-added services, but it is not easy to reach Apple's level in the short term. Therefore, the price war is intensifying. According to a mobile phone brand practitioner, most large smartphone manufacturers have gross margins between 10% and 15%, which can only cover the company's daily operating costs. Wu Lingyun lamented to reporters that there were already smartphones with a price of 199 yuan on the market last year. Although this is an extreme case, compared with feature phones, the price of smartphones in free fall has fallen more rapidly. Seemingly infinitely beautiful and prosperous market, Chinese smartphone manufacturers are still waiting for a good result. Qualcomm's advantage will weaken "Although there are some complaints, it can only be bitten." The insider described the reaction of Chinese smartphone manufacturers to Qualcomm's patent fees. On the other hand, patent bargaining power of Chinese smartphone manufacturers is generally not high. "It is understood that Apple, Samsung and other manufacturers pay Qualcomm much cheaper than domestic manufacturers, but this is legal and reasonable." Wu Lingyun and the above insiders both admit this. A domestic intellectual property expert interviewed by the reporter also said that patent owners have the right to use all patents, and Qualcomm cannot blame it on this point. Under the heavy burden of patent fees, some mobile phone manufacturers have played a "side-scattering ball", such as "declaring with low-profile models, so that the price of the whole machine is low, and the proportion of patent fees paid is small". This kind of approach disclosed by the insider makes people feel the huge cost pressure and helplessness of the manufacturers, and the large patent holders such as Qualcomm have restrained the Chinese smartphone industry. "The arrival of 4G can change this situation." This is a point that many people in the industry firmly believe. "2013 is a 4G year, and global LTE smartphone shipments will exceed 250 million units for the first time in the first quarter." Strategy AnalyTIcs director Neil Mossen believes that equipment manufacturers will benefit greatly. In the 4G era, LTE patents are highly dispersed, and no one can be the only one. This will inevitably lead to a competitive situation where multiple chip providers are evenly matched. Senior industry expert Sun Changxu said that both MediaTek and Intel will grow into strong opponents of Qualcomm, and their respective advantages are obvious. As a local company, MediaTek is highly sensitive to the Chinese market, has a good grasp, fast response, flexible and timely technical support, and the project can be mass-produced quickly, which can benefit manufacturers in the short term. Intel relies on a strong technical reserve, and its performance and power consumption have improved faster than the industry expected, and is expected to be successful in 2014 ~ 2015. In addition, Chinese manufacturers have greatly increased their right to speak on the LTE standard. Taking Huawei as an example, Huawei ’s official website shows that Huawei currently has 13.5% of LTE core patents and has submitted more than 800 LTE proposals to 3GPP. The number of patents in the LTE field Ranked third in the world. This will greatly enhance the patent gaming chips of Chinese manufacturers in the 4G era. With the acceleration of China's 4G process, the big cake that Chinese smartphone manufacturers are sticking to is in sight, and the shackles of patent fees that they hope to get rid of are expected to break. Traffic Facilities,Waterproof Traffic Facilities,Outdoor Traffic Facilities,Traffic Control Devices Yangzhou Heli Photoelectric Co., Ltd. , https://www.heli-eee.com