Regulations for the protection of power monitoring systems Chapter 1 General Provisions Article 1 In order to strengthen the information security management of power monitoring systems, prevent attacks and infringements on hackers and malicious code from power monitoring systems, and ensure the safe and stable operation of power systems, according to The Regulations, the Regulations of the People's Republic of China on the Safety and Protection of Computer Information Systems and the relevant regulations of the State, in conjunction with the actual conditions of the power monitoring system, have formulated these provisions. 1. Electrical Laminated Wood is widely used as insulating and supporting material in transformers and instrument transformers. It has many virtues such as moderate specific gravity, high mechanical properties, easy vacuum drying, easy mechanical processing etc. The dielectric constant of this material is close to transformer oil, so it makes a reasonable insulation match. And it can be used in transformer oil of 105℃ for long time. Electrical Laminated Wood Electrical Laminated Wood,Birch Plywood Sheets,Birch Laminated Wood,Electrical Birch Plywood Yingkou Dongyuan Electrical Insulation Board Co.,Ltd , https://www.dy-insulation.com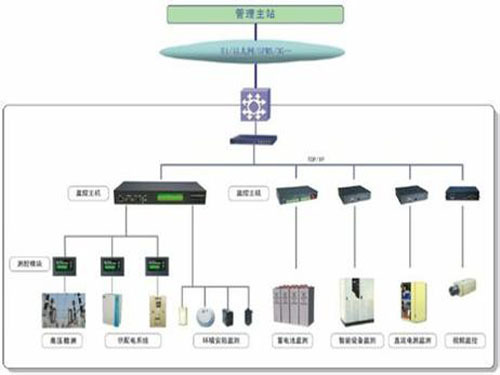
Article 2 The safety protection work of the power monitoring system shall implement the national information security level protection system. In accordance with the relevant requirements of the national information security level protection, it shall adhere to the principles of “safety zoning, network-specific, horizontal quarantine, and vertical authentication†to ensure the power monitoring system. Safety.
Article 3 The term "power monitoring system" as used in these Regulations refers to the business systems and intelligent devices based on computers and network technologies used to monitor and control the production and supply of electricity, as well as communications and data networks that are used as a basis for support.
Article 4 This regulation applies to power generation enterprises, power grid companies and related planning and design, construction and construction, installation and commissioning, research and development and other units.
Article 5 The National Energy Administration and its dispatched agencies shall supervise and administer the safety protection work of the power monitoring system.
Chapter II Technical Management Article 6 The business systems based on computers and network technologies within power generation enterprises and power grid companies shall be divided into production control regions and management information regions. The connection zone between the safe access area and other parts of the production control area must be set up with a dedicated horizontal one-way safety isolation device that has been tested and certified by the national designated department.
Article 10 A vertical power encryption authentication device or encryption authentication gateway and corresponding facilities that have been tested and certified by a designated department of the State shall be installed at the longitudinal connection between the production control area and the wide area network.
Article 11 The boundary of the safe area shall take necessary security measures and prohibit any general-purpose network service that crosses the boundary between the production control area and the management information area. The business systems in the production control area should have high security and high reliability, and the use of general-purpose network service functions with high security risks is prohibited.
Article 12 A distributed power dispatch digital certificate and security label based on public key technology shall be established in accordance with the power dispatch management system. The important business systems in the production control area shall adopt the authentication and encryption mechanism.
Article 13 In the selection and configuration of equipment, the power monitoring system shall prohibit the selection of systems and equipment that have been identified by relevant state regulatory agencies and notified of the existence of loopholes and risks by the National Energy Administration; for systems and equipment that have already been put into operation, In accordance with the requirements of the National Energy Administration and its dispatched agencies, the company must carry out timely rectification, and at the same time strengthen the operation management and safety protection of related systems and equipment. In areas of production control other than safe access areas, equipment with wireless communication capabilities should be prohibited.
Chapter III Safety Management Article 14 The safety protection of the electric power monitoring system is an integral part of the electric safety production management system. The power company shall establish and improve the safety protection management system for the power monitoring system in accordance with the principle of “who is responsible for the person responsible and who is responsible for the operationâ€, integrates the safety protection work of the power monitoring system and its information submission into the daily safety production management system, and implements the responsibility for the classification. The responsibility system.
The power dispatching agency is responsible for the technical supervision of the safety monitoring of the power monitoring system of the next-level power dispatching institutions, substations, and power plants within the scope of direct dispatch. The safety protection of other monitoring systems within the power plant can be implemented by its superior supervisory unit. Supervision.
Article 15 The implementation plan for the safety protection of the power monitoring system of the power dispatching agencies, power plants, substations and other operating units must be reviewed by the superior professional management department, the information security management department, and the corresponding power dispatching agency of the enterprise. Accepted by the above institutions. Access to power dispatch data network equipment and application systems, access technology solutions and security protection measures must be agreed by the directly responsible power dispatching agencies.
Article 16 Establish and improve the safety protection assessment system for the power monitoring system, and adopt a self-assessment-based approach and supplement the inspection and evaluation approach to incorporate the safety monitoring assessment of the power monitoring system into the power system safety assessment system. Article 17 Establish a sound joint protection and emergency response mechanism for the safety of the electric power monitoring system and formulate an emergency plan. The power dispatching agency is responsible for the unified and safe emergency management of the power monitoring system within the scope of command and dispatch.
In the event of an abnormality or failure in the power monitoring system of a production-controlled region when subjected to a cyber attack, they shall immediately report to their superior power dispatching agencies and the local national energy bureaus, and jointly take emergency protective measures to prevent the situation from expanding. At the same time, attention shall be paid. Protect the site for investigation and evidence collection.
Chapter IV Confidentiality Management Article 18 The development units and suppliers of power monitoring system-related equipment and systems shall ensure that the equipment and systems they provide comply with the requirements of this regulation by means of contractual terms or confidentiality agreements, and It is responsible for its entire life cycle. The development units, users, and suppliers of special security products for power monitoring systems shall perform confidentiality work in accordance with relevant national requirements and prohibit the proliferation of key technologies and equipment.
Article 19 All evaluation data and assessment results of the safety assessment of production control regions shall be subject to confidentiality work in accordance with the relevant requirements of the State.
Chapter V Supervision and Administration Article 20 The National Energy Administration and its dispatched offices shall be responsible for the formulation of safety management-related management and technical specifications for power monitoring systems and shall supervise their implementation.
Article 21 Where a company does not comply with the requirements of this regulation, the relevant entity shall rectify it within the stipulated time limit; if it has not been rectified within the prescribed time limit, the National Energy Administration and its dispatched organization shall be punished in accordance with relevant state regulations.
Article 22 If a violation of this provision results in a failure of the power monitoring system, it shall be handled by its superior entity in accordance with the relevant regulations; in the event of an electrical equipment accident or an electrical safety accident (event), the relevant accident (event) according to the state The investigation rules are processed.
Chapter VI Supplementary Provisions Article 23 The meanings or scopes of the following terms in this Regulation: (1) The power monitoring system specifically includes the power data acquisition and monitoring system, energy management system, substation automation system, converter station computer monitoring system, and power plant Computer monitoring system, distribution automation system, microcomputer relay protection and safety automatic device, wide area phasor measurement system, load control system, water leveling automation system and water elevator level dispatching automation system, electric energy metering system, assistance in real-time power market Control systems, power dispatch data networks, etc. (2) The power dispatch data network refers to the special-purpose wide-area data network for power dispatch at all levels and the special dialing network for power production. (3) Control zone refers to a security zone composed of real-time sub-networks or dedicated channels with real-time monitoring functions and vertical connection and use of power dispatch data networks. (IV) Non-control zones refer to the safety of various business systems in the non-real-time sub-networks that are operated on-line but are not directly involved in control and are a necessary part of the power production process and are connected to the power distribution data network in a vertical direction within the scope of production control. area.
Article 24 This regulation shall come into force on September 1, 2014. On December 20th, 2004, the "Regulations on the Protection of Power Secondary Systems" issued by the former State Electricity Regulatory Commission (Order No. 5 of the State Electricity Regulatory Commission) was repealed at the same time.
2. People usually use this material to make upper/lower pressure pieces, cable supporting beams, limbs, spacer blocks in oil-immersed transformers, and clamps in instrument transformers. It replaced steel plates, insulating paper sheets, epoxy paper sheets, epoxide woven glass fabric lamination in these fields, and cut down the material expenses and weight of transformers.
3. The raw materials of electrical laminated wood are high quality birch and willow timbers. After boiling, rotary cutting, drying, these timbers are made to veneers. At last the veneers will be glued with special insulating gluewater and processed under high temperature and pressure.